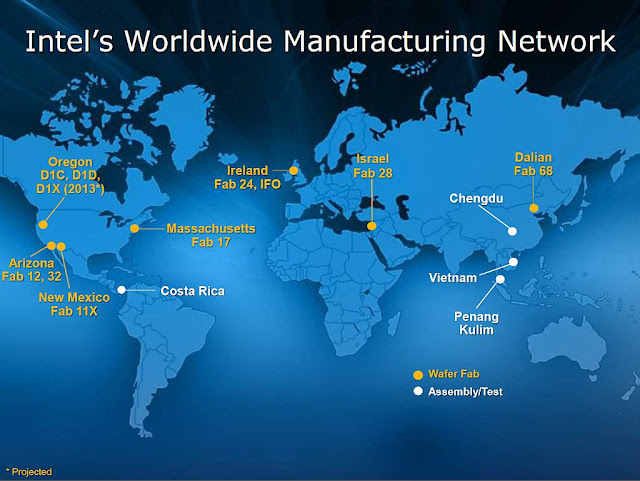
The semiconductor industry is at a critical juncture, driven by the dual pressures of rising demand for advanced chips in artificial intelligence (AI) and the urgent need to mitigate geopolitical vulnerabilities. With Taiwan’s fabs, particularly TSMC, supplying over 90% of the world’s cutting-edge semiconductors, nations are rapidly investing in new fabs to reduce reliance on both Taiwan and China. While TSMC, Samsung, and Intel lead efforts to expand capacity in regions like the US, Europe, and Japan, these initiatives fall short of replacing Taiwan’s unparalleled output of 2 nm and below chips by 2030. Simultaneously, China’s struggle to compete at leading-edge nodes, compounded by export restrictions on critical tools, further underscores the fragility of the global semiconductor supply chain. These dynamics signal a transformative era as the free world works to establish more resilient and geographically diversified semiconductor ecosystems.
According to a recent article by FT (Source), the primary drivers for 2 nm technology development are the surging demand for custom and specialized chips, particularly in artificial intelligence (AI), and the need to create competitive alternatives to current large-scale semiconductor manufacturers. Rapidus, for instance, is targeting a niche in the AI market by producing bespoke chips that prioritize efficiency and can outperform more generic chips, such as those produced by Nvidia, in specific applications.
The motivation also includes addressing capacity limitations from dominant players like TSMC, which prioritizes large orders. Rapidus sees an opportunity to capture smaller customers who are willing to pay a premium for speed and customization. Additionally, geopolitical factors are influencing the push for advanced technology, with Japan aiming to reduce reliance on Taiwan's semiconductor manufacturing expertise and establish its own ecosystem for leading-edge production.
This is why the semiconductor industry is advancing rapidly toward 3 nm and 2 nm process nodes, with leading players outlining production timelines and capacity expansions over the next five years. Below is a detailed overview of these developments, including plans from TSMC, Samsung, Intel, and Rapidus.

The forecast predicts a 540% growth in the global AI semiconductor market between 2020 and 2030, driven by increasing adoption across key segments such as servers, networking, edge devices, and PCs/smartphones. Servers are projected to dominate the market, reflecting the growing demand for AI in data centers and cloud computing, while networking and edge computing are expected to see rapid expansion, driven by real-time processing needs in IoT and automotive applications. Moderate growth is anticipated in the PCs/smartphone segment as AI integration in consumer electronics continues. Tokyo’s recent $65 billion investment in AI and semiconductor industries underscores the importance of this market, which is expected to exceed $400 billion by 2030, highlighting the transformative role of semiconductors in powering AI advancements across industries.
TSMC
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) is enhancing its semiconductor fabrication capabilities globally, focusing on 3 nm and 2 nm and below nodes.
-
3 nm Production (Taiwan): TSMC began volume production of its 3 nm process technology in December 2022 at Fab 18, located in the Southern Taiwan Science Park (STSP). Fab 18 consists of eight phases, each featuring a cleanroom area of 58,000 square meters, roughly double the size of a standard logic fab. TSMC has invested over NT$1.86 trillion in Fab 18, creating more than 11,300 high-tech jobs.
-
2 nm Development (Taiwan): TSMC’s 2 nm process is scheduled for risk production in late 2024 and mass production in 2025. A new facility in Hsinchu Science Park is under construction, with equipment installation set for April 2024.
-
2 nm (Arizona, USA): TSMC is building a second fab in Arizona to produce 2 nm nodes, with production expected to begin in 2028. A third fab, focused on cutting-edge technologies, is planned for later this decade. This is part of a $40 billion investment, the largest foreign investment in Arizona's history.
Samsung
Samsung Electronics is expanding its semiconductor manufacturing capabilities in South Korea and the United States, focusing on 3 nm and 2 nm nodes.
-
3 nm Production (South Korea): Samsung began mass production of its first-generation 3 nm chips in the second half of 2022, using its proprietary Multi-Bridge Channel Field-Effect Transistor (MBCFET) technology, a Gate-All-Around (GAA) architecture. Second-generation 3 nm production began in 2023, offering improved energy efficiency and performance.
-
2 nm Development (South Korea): Samsung plans to start 2 nm production in 2025 for mobile devices, followed by high-performance computing in 2026 and automotive semiconductors by 2027. The 2 nm (SF2) process is expected to deliver a 12% performance increase, 25% power efficiency improvement, and 5% area reduction compared to 3 nm.
-
Taylor Fab (Texas, USA): Samsung is constructing a $17 billion fab in Taylor, Texas. Initially planned for 4 nm production in late 2024, the fab may start directly with 2 nm technology in 2026 to align with Samsung’s broader roadmap.
Intel
Intel Corporation is investing in global semiconductor manufacturing, focusing on advanced nodes like Intel 3, Intel 20A, and Intel 18A.
-
United States: Intel’s Fab 42 in Arizona produces 10 nm chips and is transitioning to Intel 7 and Intel 4 nodes. In Ohio, Intel is building two fabs with a $20 billion investment to produce Intel 18A by the decade's end.
-
Europe: Intel’s Fab 34 in Ireland will produce Intel 4 technology using EUV lithography. In Germany, Intel delayed its is investing €17 billion to construct two fabs in Magdeburg, focusing on advanced nodes.
-
Israel: Intel’s Fab 28 in Kiryat Gat, Israel, is transitioning from 10 nm to Intel 7 and Intel 4 processes. Intel has committed $10 billion to expand this facility.
Rapidus
Rapidus, a Japanese semiconductor start-up, aims to produce 2 nm chips, positioning itself as a significant player in the advanced semiconductor market.
-
2 nm Development: Rapidus plans to start trial production of 2 nm chips in April 2025, with mass production by 2027. The company is collaborating with IBM to integrate cutting-edge technology, including Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) lithography.
-
Manufacturing Facilities: Rapidus is building its IIM-1 fab in Chitose City, Hokkaido, Japan. The first EUV machine from ASML is expected to arrive in mid-December 2024.
-
Strategic Approach: Rapidus is rethinking traditional manufacturing models by emphasizing smaller batch production with faster cycle times, aiming for greater efficiency and adaptability.
SMIC
China’s stake in leading-edge semiconductor manufacturing and AI is hindered by significant technological and geopolitical challenges. While domestic efforts, such as those by SMIC, have made strides in producing 7 nm chips, China remains far behind global leaders like TSMC, Samsung, and Intel, who are advancing toward 2 nm production. Critical dependencies on foreign equipment, such as ASML's EUV lithography machines, and U.S.-led export restrictions on advanced semiconductor tools and high-performance GPUs have further constrained its progress. Although China has invested heavily in AI development, its capabilities remain primarily focused on practical applications like surveillance and automation rather than leading innovation in foundational AI technologies. To conclude, China has an uphill battle to compete in the global semiconductor and AI industries.
Is the free world Decoupling from China and future risk of relying on Taiwan Fabs?
The global semiconductor industry is undergoing significant restructuring as it increasingly decouples from China and prepares for potential decoupling from Taiwan’s fabs. Geopolitical tensions, driven by concerns over China's ambitions toward Taiwan and its own restricted access to advanced chip-making technologies, have accelerated efforts by the US, Europe, and their allies to diversify supply chains and reduce dependency on both regions. Export controls targeting China, including restrictions on advanced chips and manufacturing tools, have prompted heavy investments in domestic semiconductor manufacturing in the US, Japan, South Korea, and Europe. Simultaneously, Taiwan’s pivotal role in leading-edge semiconductor production, dominated by TSMC, has highlighted vulnerabilities, spurring new fabs outside the island, such as TSMC’s facilities in Arizona and Samsung’s in Texas. These shifts reflect a broader trend toward creating more resilient, geographically dispersed semiconductor ecosystems that mitigate risks associated with reliance on any single region for critical technologies.
Current global plans for semiconductor manufacturing expansion aim to reduce dependency on Taiwan but fall short of ensuring sufficient non-Taiwan capacity for 2 nm and below nodes in the near term. Taiwan, led by TSMC, still dominates leading-edge semiconductor production, supplying over 90% of the world’s advanced chips. While significant investments are underway—such as TSMC's Arizona fabs, Samsung’s expansions in South Korea and Texas, and Intel's facilities in the US, Europe, and Israel—these efforts are unlikely to match Taiwan’s scale and technological leadership at 2 nm and below by 2027-2030.
For example, TSMC’s planned Arizona fab is projected to produce 2 nm chips by 2028, but its capacity will be a fraction of TSMC's output in Taiwan. Similarly, Samsung and Intel are progressing toward advanced nodes, but both face challenges in matching TSMC’s efficiency and yield at these cutting-edge technologies. Additionally, the complexity of EUV lithography and the industry's high R&D costs further limit the pace at which non-Taiwan fabs can scale to competitive capacities.



%20(1).png)