Thursday, April 10, 2025
AlixLabs to Demonstrate APS™ on 300-millimeter UMC wafers at the 2025 CMC Conference
Monday, February 10, 2025
AlixLabs Demonstrates 3 nanometers on Intel Silicon – Without EUV
The Swedish semiconductor company has fabricated leading-edge structures without using complex and costly lithography techniques.
The Swedish semiconductor company AlixLabs announces that it has used its technology to etch structures equivalent to commercial 3-nanometer circuits on Intel test silicon. Notably, this has been achieved without the use of extreme ultraviolet lithography (EUV) or advanced multi-patterning techniques such as SADP and SAQP (Self-Aligned Double Patterning and Self-Aligned Quad Patterning, respectively).
AlixLabs, a startup based in Lund, specializes in the development of Atomic Layer Etching (ALE), a type of plasma-based dry etching for cutting-edge structures, and ALE Pitch Splitting (APS), which enables transistor fins to be split using etching. The advantage of this approach is that it significantly reduces costs at the cutting edge, where wafer prices skyrocket with each new generation.
"We are pleased to demonstrate how APS can help the industry reduce its dependence on multi-patterning while lowering costs and environmental impact. Our technology enables the fabrication of sub-10-nanometer structures on silicon, and through Intel’s Test Vehicle Program, we have proven that sub-5-nanometer structures can be achieved using etching alone."– Dmitry Suyatin, CTO and Co-Founder of AlixLabs
According to Dmitry Suyatin, AlixLabs’ CTO, this demonstration was made possible through Intel’s Test Vehicle Program, which provided test silicon for AlixLabs to process with its APS technology. While ALE has traditionally been limited to structures in the 10-nanometer class, AlixLabs' APS technique has significantly simplified the manufacturing of structures smaller than 5 nanometers.
Etching 3-nanometer-class structures without advanced EUV lithography, using only immersion lithography, is a significant breakthrough—provided the technology can be scaled and applied in practical manufacturing. AlixLabs has previously stated its goal of seeing its technology adopted by TSMC and Samsung for their 2-nanometer processes.
Since the industry moved past the 28-nanometer node, multi-patterning has become increasingly necessary to create smaller structures and transistors. This lithographic technique involves breaking down complex patterns into simpler ones and sequentially patterning them onto the silicon wafer for higher precision and detail. Lithography can perform this in two, three, or four steps (SADP, SAQP), though more steps are theoretically possible, they are considered too complex and costly for practical use at smaller nodes.
"APS technology demonstrates that complex multi-patterning techniques such as SADP and SAQP are not needed to manufacture circuits at 5 nanometers and below. This increases the potential to use immersion lithography for critical mask layers in 3-nanometer processes. These results were achieved with our early Alpha equipment, and Beta equipment will follow later in 2025. We thank Intel for enabling this demonstration and providing high-quality test silicon."– Jonas Sundqvist, CEO and Co-Founder of AlixLabs
While lithographic multi-patterning is often necessary, it comes with several downsides. Each additional step requires more masks, which must be precisely aligned to form the final, complex pattern. Even a slight misalignment can lower yield and performance, but more importantly, it significantly extends production time. Avoiding multi-patterning whenever possible is therefore always preferable.
It is essential to distinguish between "nanometer-class" structures and actual physical nanometer measurements. What AlixLabs has achieved is a metal pitch (the distance between metal interconnects connecting transistor gates) of 25 nanometers through dry etching. This compares to TSMC’s most advanced 3-nanometer process, which achieves a metal pitch as low as 23 nanometers in certain high-density configurations.
AlixLabs highlights this test silicon as a major milestone towards commercialization and announces that more updates will follow later in 2025. Additional details will be presented by CTO Dmitry Suyatin at SPIE Advanced Lithography + Patterning in San Jose, California, on February 27, from 9:00–9:20 AM (local time).
Sources:
AlixLabs demonsterar 3 nanometer på Intel-kisel – utan EUV – Semi14
AlixLabs to Showcase Latest APS™ Findings at SPIE Advanced Lithography + Patterning – AlixLabs
Browse the 2025 program for SPIE Advanced Lithography + Patterning
Thursday, January 30, 2025
Lam Research’s Dry Resist: A Breakthrough in EUV Lithography for Next-Generation Logic and Memory Manufacturing
Lam Research’s dry resist technology represents a major shift in EUV lithography and semiconductor patterning, addressing critical challenges such as stochastic defectivity, resolution limitations, and cost-efficiency. With recent qualifications for advanced DRAM and 2nm logic manufacturing, along with a growing ecosystem for high-volume production, dry resist is positioned to disrupt traditional chemically amplified resists (CARs) and enable future High-NA EUV adoption.
One of the most significant recent developments is Lam’s qualification of dry resist for 28nm pitch BEOL logic at 2nm and below in collaboration with imec. This qualification confirms that dry resist can eliminate multi-patterning steps, reducing complexity and improving EUV throughput. The process is designed to work with both low-NA and high-NA EUV scanners, ensuring its relevance for sub-2nm logic scaling. This represents a key milestone in extending direct EUV printing to future logic nodes, an approach that could significantly lower lithography costs while improving pattern fidelity.
In addition, a leading DRAM manufacturer has selected Lam’s Aether dry resist technology as its production tool of record for advanced DRAM nodes. This decision highlights dry resist’s low-defect, high-fidelity patterning capabilities, which are essential for scaling memory architectures. The technology enables lower exposure doses while reducing stochastic defects, which are a major concern in EUV-based DRAM production. Given that Samsung, SK Hynix, and Micron are all increasing their reliance on EUV for next-generation DRAM, Lam’s dry resist is well-positioned for widespread adoption in the memory sector.
To ensure a stable supply chain for dry resist materials, Lam Research has partnered with Entegris and Gelest, a Mitsubishi Chemical Group company. This collaboration ensures reliable dual-source precursor production, providing chipmakers with long-term process stability. The partnership also focuses on the development of next-generation high-NA EUV precursors, further strengthening dry resist’s role in future sub-2nm manufacturing.
SEM images of 28 nm pitch line/space patterns imaged with 0.33NA EUV in dry resist from Entegris precursor.
A critical enabler of dry resist technology is its atomic layer deposition (ALD) process, which replaces traditional spin-coating used in CARs. ALD-based vapor-phase deposition offers higher uniformity, eliminating polymer chain variations found in conventional resists. It also allows precise thickness control, which is essential for optimizing EUV photon absorption and etch selectivity. Unlike CARs, which rely on a complex mixture of polymers, dry resist materials are based on single-component metal-organic precursors such as organo-tin oxides. These materials provide higher EUV photon absorption, improving sensitivity and pattern resolution.
Another key advantage of dry resist is its anisotropic dry development process, which replaces wet solvent-based development. Traditional CAR-based EUV resists require organic solvents or aqueous bases, leading to stochastic defects, material loss, and waste. Dry resist, by contrast, is developed entirely in the gas phase, selectively removing unexposed regions and forming a negative-tone image. This eliminates line collapse and delamination issues, improving yield stability. Additionally, the elimination of wet chemistries significantly reduces chemical waste, making dry resist a more sustainable solution with five to ten times lower material consumption compared to traditional resists.
Lam’s dry resist technology is poised to disrupt traditional CAR-based EUV lithography, particularly as the industry moves toward High-NA EUV adoption. By reducing multi-patterning dependency, the technology enhances cost-effective EUV scaling, making it an attractive solution for both logic and memory manufacturers. This positions Lam as a key leader in next-generation EUV resist solutions, challenging conventional resist suppliers like JSR, TOK, and Inpria.
From a sustainability perspective, dry resist significantly lowers EUV exposure dose requirements, leading to higher scanner throughput and lower energy consumption. Its reduced defectivity translates to higher yield per wafer, further enhancing cost-efficiency. The collaboration with Entegris and Gelest ensures supply-chain stability, making dry resist a viable and scalable technology for sub-2nm nodes.
Sources:
Saturday, December 14, 2024
Intel Unveils 6 nm Gate Length Silicon RibbonFET CMOS and Breakthroughs in Semiconductor Scaling at IEDM 2024
Intel Corporation / Intel Foundry has demonstrated and extensively characterized gate-all-around Silicon RibbonFET CMOS transistors with a 6 nm gate length (LG). The study showcases nanoribbon silicon thickness (Tsi) scaling down to 3 nm, enhancing short-channel effects without compromising performance. Effective workfunction engineering mitigates threshold voltage increases caused by quantum confinement at scaled Tsi, enabling reduced threshold voltage at highly scaled gate lengths. Injection velocity of 1.13x10^7 cm/s is maintained at LG=6nm without degradation down to Tsi=3 nm, highlighting advancements crucial for continued gate length scaling and the ongoing realization of Moore's Law.
Intel Foundry made groundbreaking announcements at the IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) 2024, showcasing advancements that propel semiconductor technology into the next decade and beyond. Highlights include innovations in transistor and interconnect scaling, advanced packaging, and emerging materials to support the industry’s roadmap toward achieving 1 trillion transistors on a chip by 2030. Intel demonstrated a 25% capacitance reduction using subtractive ruthenium for interconnections, achieved a 100x throughput improvement in advanced packaging through Selective Layer Transfer (SLT), and advanced gate-all-around (GAA) transistor scaling with Silicon RibbonFET CMOS at a 6 nm gate length. Additionally, Intel unveiled new work on gate oxide modules for scaled 2D FETs, addressing the next phase of GAA scaling.
Among the key technical breakthroughs, subtractive ruthenium stands out as a metallization alternative to copper for interconnects, offering significant capacitance reductions at tight pitches while being cost-effective and scalable for high-volume manufacturing. SLT further revolutionizes advanced packaging with ultra-fast, flexible chip-to-chip assembly, enabling smaller, higher-density chiplets for AI and other demanding applications. For transistor scaling, Intel’s demonstration of Silicon RibbonFET CMOS at 6 nm gate length delivers industry-leading short-channel effects and performance, paving the way for continued scaling under Moore’s Law. Additionally, Intel’s progress with 2D GAA NMOS and PMOS transistors and gate oxide development signals readiness for post-silicon semiconductor technologies.
Intel also highlighted progress in gallium nitride (GaN) technology, demonstrating the first 300 mm GaN-on-TRSOI substrates for high-performance power and RF electronics. These developments, alongside Intel’s continued focus on advanced memory integration, hybrid bonding, and modular system expansion, underscore its commitment to addressing challenges in AI, energy efficiency, and thermal management. With these innovations, Intel Foundry continues to lead the charge in semiconductor advancements, ensuring a robust path forward for the trillion-transistor era.
Source: Intel IEDM 2024 Innovations
Friday, November 8, 2024
New Method for Precision Doping in 2D Semiconductors Enables Next-Gen CMOS Integration
Preparation of the Mo Film: Initially, thin Mo films are deposited on a silicon/silicon dioxide (Si/SiO2) substrate using magnetron co-sputtering. During this step, controlled amounts of Nb (for p-type doping) or Re (for n-type doping) are co-sputtered with the Mo film, resulting in a doped Mo layer.Tellurization Process in the CVD Reactor: The Mo film, now doped with Nb or Re, is placed in a CVD furnace along with solid tellurium (Te) lumps. Under a controlled flow of carrier gases (argon and hydrogen), the CVD chamber is heated to high temperatures (around 650°C). The Te vapor reacts with the Mo, leading to the formation of 1T'-MoTe2.Phase Transformation to 2H-MoTe2: At the elevated temperatures within the CVD system, the 1T'-MoTe2 structure undergoes a phase transformation into the more stable 2H phase, producing the final doped 2H-MoTe2 film. This phase is crucial because 2H-MoTe2 has semiconducting properties suitable for integrated circuits.Doping Incorporation: During the CVD tellurization, Nb and Re atoms from the initial Mo film become substitutionally incorporated into the MoTe2 lattice. This incorporation determines the semiconductor type (p-type or n-type) and carrier concentration of the resulting 2H-MoTe2 film.Large-Scale Uniformity: By controlling the initial dopant concentration and maintaining consistent conditions in the CVD process, the researchers achieved uniform doping across large-scale wafers, crucial for creating reliable semiconductor devices.
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
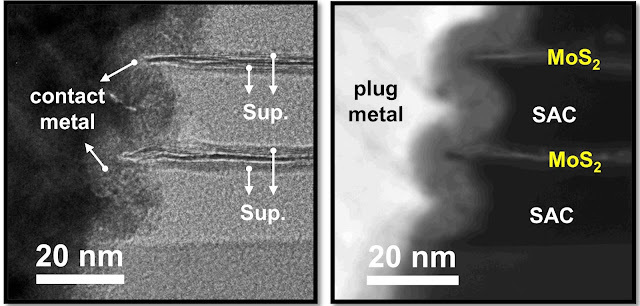
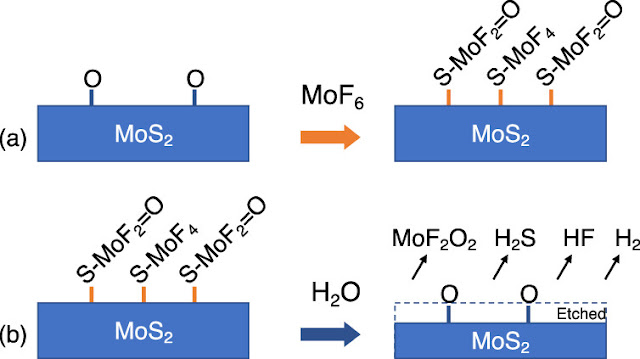
Intel Sets Record with 2D TMD Transistors for Next-Gen Electronics
Friday, September 13, 2024
AlixLabs Qualifies APS™ for Use In 300-millimeter Silicon Wafer Designs
AlixLabs' patented and wordmarked APS™ IP – short for Atomic Layer Etch (ALE) Pitch Splitting, here demonstrated in a simple animation.
“Proving that APS™ works on lithography designs on 300-millimeter wafers, is what we’ve all worked on since we founded AlixLabs in 2019,” says CEO and co-founder Dr. Jonas Sundqvist. “Not only do we aim to provide chip manufacturers wafer processing equipment that can create 20-nanometer half-pitch lines and critical dimension below 15 nanometers on silicon, we aim to do that at a lower cost and a more sustainable way than other technologies”
“We are also able to provide record breaking 3-nanometer critical dimension features on gallium phosphide (GaP) wafers today showing that APS™ can scale far into the future beyond what is needed today,” adds CTO and co-founder Dmitry Suyatin.
Sunday, June 16, 2024
ASML Unveils Hyper-NA EUV: Pioneering New Frontiers in Chip Innovation and Efficiency
Monday, January 8, 2024
Intel Receives ASML's First High-NA EUV Lithography Scanner, Pioneering Next-Gen Semiconductor Manufacturing
ASML has delivered its groundbreaking High-NA EUV lithography scanner, the Twinscan EXE:5000, to Intel Oregon. Marking a significant technological leap, this first-of-its-kind scanner boasts a 0.55 NA lens, enabling 8nm resolution for advanced semiconductor manufacturing. Designed for process technologies beyond 3nm, it promises to enhance chip production efficiency and reduce costs. Intel's early adoption of this state-of-the-art equipment, valued between $300-$400 million, positions them at the forefront of the industry, potentially setting new standards in High-NA manufacturing. This development represents a major milestone in semiconductor technology, signaling a new era of innovation and capability in chip production.
Friday, December 29, 2023
TSMC Set to Revolutionize Chip Technology with Trillion-Transistor Packages by 2030
Monday, December 11, 2023
Intel Showcases Groundbreaking Transistor Innovations at IEDM 2023
At the 2023 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), Intel introduced significant advancements in transistor technology that continue to drive Moore's Law forward. Intel's Components Research group demonstrated innovative 3D stacked CMOS transistors, enhanced with backside power and direct backside contacts. This breakthrough in transistor architecture allows for more efficient scaling and improved performance, marking a first in the industry.
3D Stacked CMOS Transistors
Intel displayed the ability to vertically stack complementary field effect transistors (CFET) with a scaled gate pitch down to 60 nanometers (nm). This technology, combined with backside power and direct backside contacts, underscores Intel's leadership in gate-all-around transistors and its capacity to innovate beyond RibbonFET.
Beyond Five Nodes in Four Years
Intel's PowerVia, set for manufacturing readiness in 2024, represents the first implementation of backside power delivery. At IEDM 2023, the company identified ways to extend and scale backside power delivery beyond PowerVia, utilizing backside contacts and other novel vertical interconnects for efficient device stacking.
Integration of Silicon and GaN Transistors
Intel successfully integrated silicon transistors with gallium nitride (GaN) transistors on the same 300 mm wafer. The "DrGaN" technology showcased at the event demonstrates Intel's advancements in high-performance integrated circuits for power delivery.
Advances in 2D Transistor Space
Intel presented high-mobility transition metal dichalcogenide (TMD) 2D channel materials, showcasing prototypes of high-mobility TMD transistors for both NMOS and PMOS. Additionally, Intel revealed the world’s first gate-all-around (GAA) 2D TMD PMOS transistor and the first 2D PMOS transistor fabricated on a 300 mm wafer.
These developments by Intel represent a significant stride in semiconductor research, promising to enhance the efficiency and capabilities of future computing technologies.
Friday, December 8, 2023
IBM and Samsung Revolutionize Semiconductor Industry with Groundbreaking VTFET Transistor Technology
Monday, October 23, 2023
TSMC To Report Breakthrough in NMOS Nanosheets Using Ultra-Thin MoS2 Channels at IEDM 2023
Monday, September 26, 2022
Bottom-up PEALD of SiO2 by growth inhibition for seamless gap-fill process
Bottom-up plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition of SiO2 by utilizing growth inhibition using NH3 plasma pre-treatment for seamless gap-fill process
Saturday, May 8, 2021
Webinar - Decadal Plan for Semiconductors: New Compute Trajectories for Energy Efficiency
Friday, April 30, 2021
The US Patent Office has approved AlixLabs’ patent application for nanofabrication by ALE Pitch Splitting (APS)
Saturday, March 6, 2021
Thermal ALE of germanium rich SiGe by CU Boulder and ASM Microchemistry
Wednesday, February 3, 2021
LIVE Stream - Advanced Process Technologies to Enable Future Devices and Scaling (invited), Rob Clark Tokyo Electron
Thursday, January 21, 2021
Master Thesis in Nanotechnology with Alixlabs in Sweden on Atomic Level Fragmentation
Thursday, December 17, 2020
Imec introduces 2D materials in the logic device scaling roadmap
More details can be found in 4 papers presented at the 2020 IEDM conference:
[1] ‘Introducing 2D-FETs in device scaling roadmap using DTCO’, Z. Ahmed et al.
[2] ‘Wafer-scale integration of double gated WS2-transistors in 300mm Si CMOS fab’, I. Asselberghs et al.
[3] ‘Dual gate synthetic WS2 MOSFETs with 120µS/µm Gm 2.7µF/cm2 capacitance and ambipolar channel’, D. Lin et al.
[4] ‘Sources of variability in scaled MoS2 FETs’, Q. Smets et al. (IEDM highlight paper)



%20(1).png)