World Water Day on 22nd March highlighted some
staggering facts about water shortages affecting much of the world’s population. While many Western countries take access to clean water for granted, growing water crises in other countries have world-wide consequences. For example, China is taking steps to secure its water resources, with severe impacts for global supply chains across multiple industries.
‘Our bodies, our cities and our industries, our agriculture and our ecosystems all depend on it,’ said UN Secretary-General António Guterres. 70-80% of all water consumption is for agriculture and energy production. Balancing the water needs of food and energy production is a challenge for many nations.
Water is also essential to mining, chemicals production, and manufacturing, industries which have long assumed ongoing, plentiful supply. This perception is changing as a deeper understanding of the water balance for each country reveals a different reality. Some countries, including China, are net water exporters: the water used to produce the goods and materials they export is higher than the water embodied in imports. Also, the production of exports often pollutes their waterways.
As water stress sets in, these countries have no choice but to change their production practices and trade balance,
disrupting global supply chains. For the past five years, the World Economic Forum has ranked water crises in its top 5 global risks in terms of impact, yet most industrial companies seem oblivious to the risks to supply chains for themselves and their customers.

Some provinces have water resources on par with the Middle East. Source: CWR LINK
Graphic media images of devastating floods from typhoons and other extreme weather events give the impression that China has plenty of water. In southern China, this is partially true, but it’s not so in the north. According to
China Water Risk, the 11 driest provinces are in northern China. Home to 38% of the population, these provinces account for 36% of agricultural output, 47% of industrial
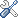
output and 43% of GDP, yet have only 7% of the country’s water resources. With a population of around 100 million, Shandong province, for example, has only 250 m3 of water per person – less than most countries in the Middle East. Less than 500 m3 of water per person is considered a critical shortage.
To meet demand, the Chinese have been extracting groundwater at unsustainably high rates. The driest 11 provinces rely on groundwater for 28% of water needs, compared to just 13% for the 13 most water-secure provinces, which are mostly in the south. If business continues as usual, water demand will exceed supply by 2030. Chinese authorities are well aware of these issues and are moving responsibly to impose the
‘three red lines’: national water quotas set for 2015, 2020 and 2030. The Made in China 2025 policy promotes high-GDP low-water industries and China is continuing its ‘war on pollution’.
The implications for China’s chemicals industries and the supply chains that depend on them are profound. For example,
China dominates global zirconium chemicals supply on which the world relies for: mobile communications, clean energy technologies, catalytic converters used in the automotive industry, jet turbines, bio-ceramic dental, knee, and hip implants, and waterproof and fire-resistant fabrics. But two-thirds of China’s zirconium chemicals production is located in the dry northern provinces, with 52% of capacity in parched Shandong.
Similarly,
China has conquered more than 90% of the rare earths market. Rare earths have multiple applications in advanced technology for transport, information, and communications, defense and medicine. Most of China’s rare earths production occurs in Inner Mongolia, where water supply is also under stress, despite relatively low population density.
So, what happens when Chinese authorities reduce or withdraw water access for zirconium and rare earths production? Or when new anti-pollution laws impose severe remediation costs on producers? Severe impacts will be felt around the world unless alternative supplies of these critical materials can be found.
Fortunately, Australia has the opportunity to secure a strategic alternative supply of zirconium, rare earths and other essential elements, for 80+ years. The world-class
Dubbo Project in central NSW has a water supply and licenses in place, and water efficiency measures include extensive recycling and optimization of product and waste streams. To progress the Dubbo Project to construction, Alkane Resources seeks a blend of financing from export credit agencies, strategic partners and equity and debt markets. Information for investors is available
here
------------------------------------
Guest Blog by Alister MacDonald, General Manager - Marketing, Alkane Resources



%20(1).png)